Economic and job growth keep plodding along as the U.S. economy enters its fifth year of recovery. The expansion is fast enough to keep the economy out of another recession, but it is still too slow to drastically reduce the high unemployment rate and create the millions of jobs that Americans desperately need.
There are clear reasons for the slow expansion, including the across-the-board federal budget cuts known as the sequester, a lingering financial crisis in Europe, slowing growth in China and elsewhere, and high gasoline prices in the United States.
These factors should push policymakers to find and enact policies that can spur faster economic growth. The first order of business should be to replace the sequester with a budget deal that focuses on promoting growth through infrastructure investments, among other investments, while reducing the threat of high federal debt levels through sensible tax reform. Federal policies should also center on making sure that particularly vulnerable groups, such as communities of color, young people, and workers without high school degrees, experience a measurable increase in economic security. Members of Congress have an opportunity to design sensible policies as part of a new budget in the coming months.
1. The economy continues to grow slowly. Gross domestic product, or GDP, increased in the second quarter of 2013 at an inflation-adjusted annual rate of 1.7 percent. Domestic consumption increased by an annual rate of 1.8 percent, housing spending substantially grew by 13.4 percent, and business investment accelerated by 4.6 percent. Exports increased by 5.4 percent in the first quarter, but government spending shrank again by 0.4 percent, slowing overall growth.
The U.S. economy was 9 percent larger in June 2013 than in June 2009 (in inflation-adjusted terms), when the recovery started. On average, however, the economy has expanded by 19.1 percent—more than twice as fast—during the first four years of a recovery, in recoveries that lasted at least four years. Fiscal austerity abroad and at home is hurting economic growth. Policy solutions should therefore aim to ease the strain of U.S. fiscal austerity on the economy and replace across-the-board spending cuts with a fiscal policy approach that can actually enhance rather than slow economic growth, while also reducing long-term deficits.
2. The moderate labor-market recovery continues in its fourth year. There were 5.3 million more jobs in June 2013 than in June 2009, when the economic recovery officially started. The private sector added 6.2 million jobs during this period. The loss of more than 660,000 state and local government jobs explains the difference between the net gain of all jobs and the private-sector gain in this period. Budget cuts reduced the number of teachers, bus drivers, firefighters, and police officers, among others. Job creation should be a top policy priority since private-sector job growth is still too weak to quickly overcome other job losses and rapidly lower the unemployment rate. A reorientation of tax and spending policies to strengthen economic growth rather than a blind obsession with deficit reduction at all costs could create millions of jobs that America’s middle class desperately needs.
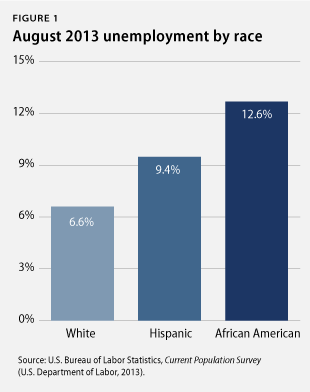
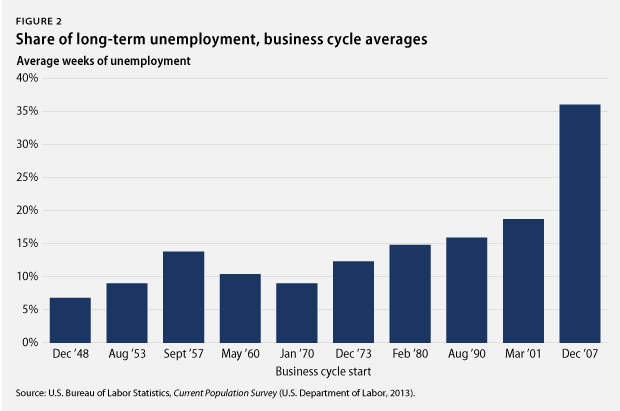
3. Long-term unemployment stays high, and some communities continue to struggle disproportionately from unemployment. The unemployment rate stood at 7.4 percent in June 2013, and 37 percent of the unemployed had been out of work for at least six months. Those out of a job for a long time struggle to regain employment because their skills atrophy. This is especially true for economically vulnerable groups. The African American unemployment rate was 12.6 percent in June 2013, the Hispanic unemployment rate was 9.4 percent, and the white unemployment rate was 6.6 percent. Meanwhile, youth unemployment stood at 23.7 percent. The unemployment rate for people without a high school diploma ticked up to 11 percent, compared to 7.6 percent for those with a high school degree, 6 percent for those with some college education, and 3.8 percent for those with a college degree. These population groups with higher unemployment rates have struggled disproportionately more amid the weak labor market than white workers, older workers, and workers with more education. Policymakers should heed the recommendations in All-In Nation—a new book from the Center for American Progress and PolicyLink—on building a strong and diverse workforce that draws from all communities.
4. The rich continue to pull away from most Americans. Incomes of households in the 95th percentile—those with incomes of $186,000 in 2011, the most recent year for which data are available—were more than nine times the incomes of households in the 20th percentile, whose incomes were $20,262. This is the largest gap between the top 5 percent and the bottom 20 percent of households since the U.S. Census Bureau started keeping record in 1967. Median inflation-adjusted household income stood at $50,054 in 2011, its lowest level in inflation-adjusted dollars since 1995. And the poverty rate remains high, at 15 percent in 2011, as the economic slump continues to take a massive toll on the most vulnerable citizens.
5. Employer-sponsored benefits disappear. The share of people with employer-sponsored health insurance dropped from 59.8 percent in 2007 to 55.1 percent in 2011, the most recent year for which data are available. The share of private-sector workers who participated in a retirement plan at work fell to 39.2 percent in 2011, down from 42 percent in 2007. Families now have less economic security than in the past due to fewer employment-based benefits, which requires that they have more private savings to make up the difference.
6. Family wealth losses still linger. In March 2013 total family wealth was down $8.4 trillion (in 2013 dollars) from March 2007, its previous peak. Homeowners on average own only 49.2 percent of their homes—compared to the long-term average of 61 percent before the Great Recession—with the rest owed to banks. Homeowners’ massive debt slows household-spending growth, as households still have little collateral for banks to loosen their lending standards and households spend less than they otherwise would on new homes and other big-ticket items.
7. Household debt is still high. Household debt equaled 106.3 percent of after-tax income in March 2013, down from a peak of 126 percent in March 2007. Household debt grew again relative to after-tax income in the first quarter of 2013, up from a low of 104.8 percent—the first such increase since the fourth quarter of 2009. A return to debt growth outpacing income growth from already-high debt levels could eventually slow economic growth again if interest rates rise from historically low levels and crowd out household spending on other items.
8. The housing market continues to recover from historic lows. New home sales amounted to an annual rate of 497,000 in June 2013—a 38.1 percent increase from the 360,000 homes sold in June 2012 but well below the historical average of 698,000 homes sold before the Great Recession. The median new-home price in May 2013 was 7.4 percent higher than one year earlier. Existing-home sales were up by 15.2 percent in June 2013 from one year earlier, and the median price for existing homes was up by 13.5 percent during the same period. Home sales have to go a lot further, given that homeownership in the United States stood at 65 percent in the second quarter of 2013, down from 68.2 percent before the recession. The current homeownership rates are similar to those recorded in 1995, well before the most recent housing bubble started. Though the housing-market recovery started later than the wider economic recovery—and started out at a record low—lately the housing market has been growing rapidly and contributing a much-needed boost to economic progress. As such, there is still plenty of room for the housing market to provide more stimulation to the economy more broadly. The fledgling housing recovery could gain further strength if policymakers support economic growth and job creation at the same time.
9. Homeowners’ distress remains high. Even though mortgage troubles have gradually eased since March 2010, nearly one in nine mortgages is still delinquent or in foreclosure. In the first quarter of 2013, the share of mortgages that were delinquent was 7.3 percent, and the share of mortgages that were in foreclosure was 3.6 percent. Many families delayed and defaulted on mortgage payments amid high unemployment and massive wealth losses. This caused some banks to be nervous about extending new mortgages, which further prolonged the economic slump. Policymakers can accelerate economic growth by helping households lower their debt burdens through refinancing help and debt forgiveness.
10. Corporate profits stay high near pre-crisis peaks. Inflation-adjusted corporate profits were 83.1 percent larger in March 2013 than in June 2009, when the economic recovery started. The after-tax corporate-profit rate—profits to total assets—stood at 3 percent in March 2013, nearing the previous peak after-tax profit rate of 3.2 percent that occurred prior to the Great Recession.
11. Slow productivity growth marks the U.S. economy. Productivity growth is the main ingredient in rising living standards. Wages, jobs, and profits depend on workers and companies figuring out how to make more and better things in the same amount of time. Output per hour, the main measure of productivity growth, has expanded by 7.4 percent from December 2007, when the Great Recession started, to March 2013, the last quarter for which data are available. This is substantially less than the average productivity growth of 9.6 percent during the same periods in previous business cycles of equal or greater length.
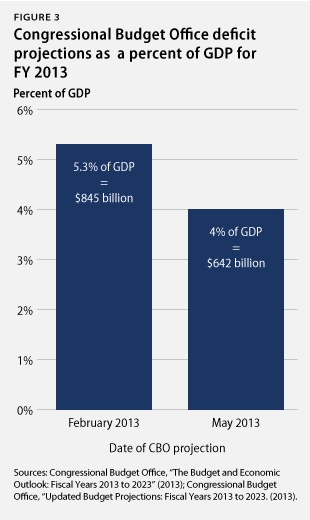
12. The outlook for budget deficits improves. The nonpartisan Congressional Budget Office, or CBO, estimated in May 2013 that the federal government will have a deficit—the difference between taxes and spending—of 4 percent of GDP for fiscal year 2013, which runs from October 1, 2012, to September 30, 2013. This deficit projection is down from 7 percent in FY 2012. This projected deficit for FY 2013 is better than what CBO predicted in February 2013, when it estimated a deficit of 5.3 percent of GDP for FY 2013. This improvement follows larger-than-expected tax collections, an improving economy, and slower health care inflation, among other factors. The estimated deficit for FY 2013 is much smaller than it was in previous years due to a number of measures that policymakers have already taken to slow spending growth and raise a little more revenue than was expected just last year. The improving fiscal outlook generates breathing room for policymakers to focus their attention on long-term growth and job creation in addition to long-term deficit reduction.
Christian E. Weller is a Senior Fellow at the Center for American Progress and a professor in the Department of Public Policy and Public Affairs at the McCormack Graduate School of Policy and Global Studies at the University of Massachusetts Boston. Sam Ungar is a Research Assistant at the Center.